Here's a preview from my zine, How Integers and Floats Work! If you want to see more comics like this, sign up for my saturday comics newsletter or browse more comics!
 get the zine!
get the zine!
read the transcript!
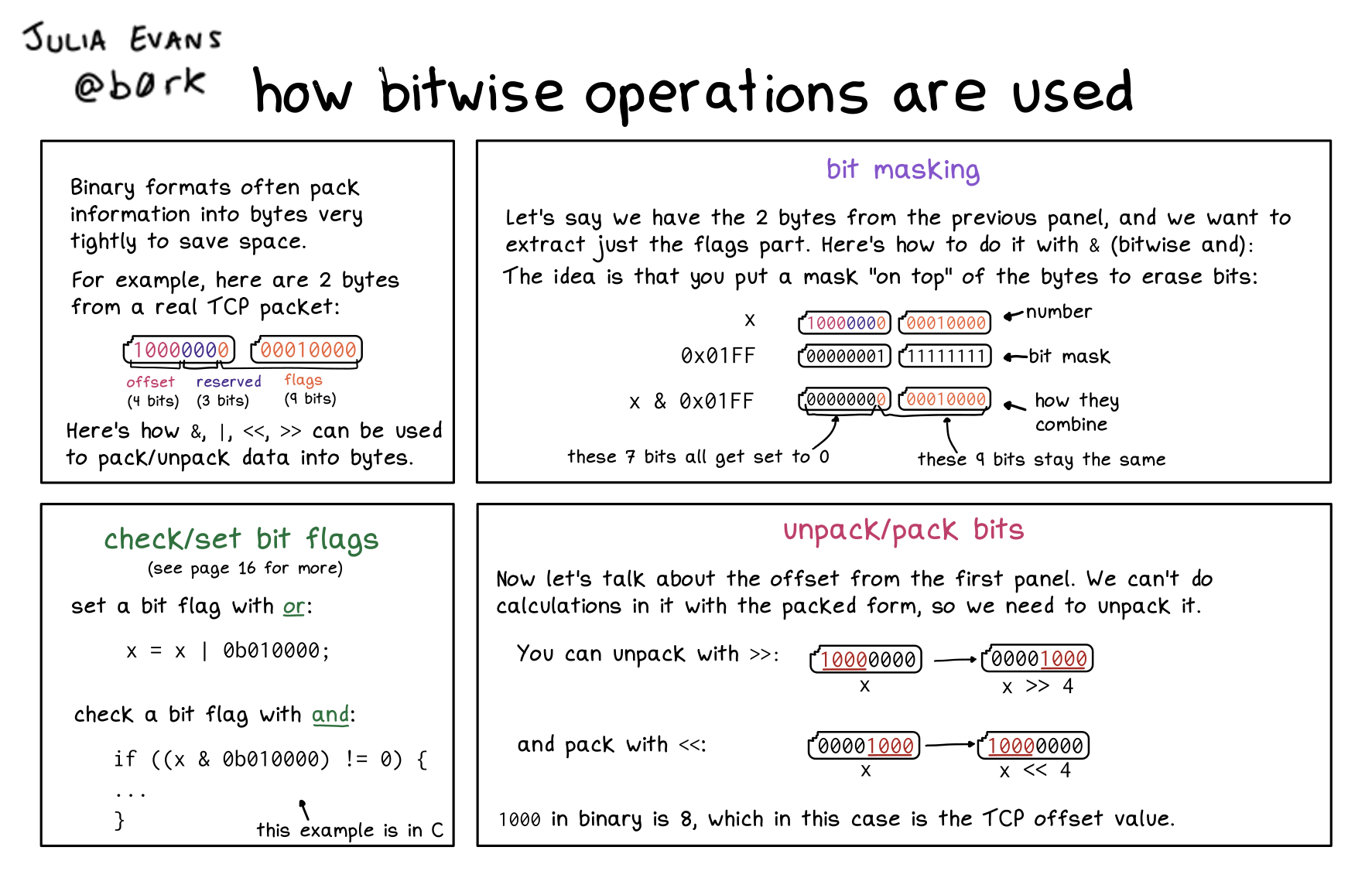
Binary formats often pack information into bytes very tightly to save space.
For example, here are 2 bytes from a real TCP packet:
10000000 00010000
The first “1000” is the offset (4 bits)
The following “000” is reserved (3 bits)
The remaining “00010000” are the flags (9 bits)
Here’s how &, |, <<, >> can be used to pack/unpack data into bytes.
bit masking
Let’s say we have the 2 bytes from the previous panel, and we want to extract just the flags part. Here’s how to do it with & (bitwise and):
The idea is that you put a mask “on top” of the bytes to erase bits:
X: 10000000 00010000 (number)
0x01FF: 000000001 1111111 (bit mask)
x & 0x01FF: 000000001 0010000 (how they combine)
000000001: these 7 bits all get set to 0
0010000: these 4 bits stay the same
check/set bit flags
(see page 16 for more)
set a bit flag with or:
x = x | 0b010000;
check a bit flag with and:
if ((x & 0b010000) != 0) {
00001000 X
}
(this example is in C)
unpack/pack bits
Now let’s talk about the offset from the first panel. We can’t do calculations in it with the packed form, so we need to unpack it.
You can unpack with »:
10000000 -> 00001000
X -> X >> 4
and pack with «:
0001000 -> 10000000
X -> X << 4
1000 in binary is 8, which in this case is the TCP offset value.