Here's a preview from my zine, How Integers and Floats Work! If you want to see more comics like this, sign up for my saturday comics newsletter or browse more comics!
 get the zine!
get the zine!
read the transcript!
integer overflow
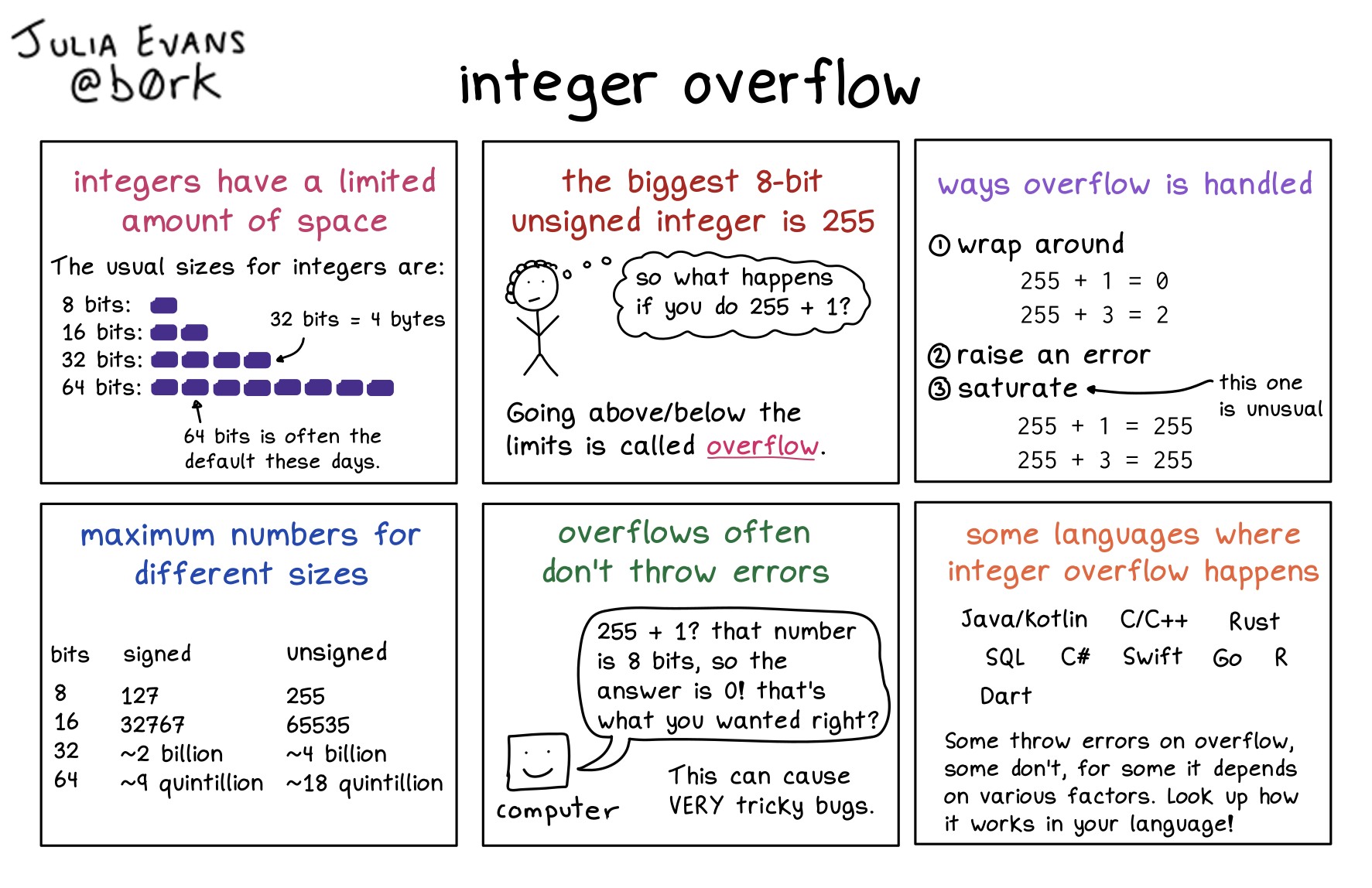
integers have a limited amount of space
The 4 usual sizes for integers are 8 bits, 16 bits, 32 bits, and 64 bits
the biggest 8-bit unsigned integer is 255
… so what happens if you do 255 + 1? going above/below the limits is called overflow
the result wraps around to the other side
255 + 1 = 0
255 + 3 = 2
200 * 2 = 144
0 - 2 = 254
maximum numbers for different sizes
bits: unsigned signed
8: 127 255
16: 32767 65535
32: 2 billion ~4 billion
64: ~9 quintillion ~18 quintillion
overflows often don’t throw errors
computer (thinking): “255 + 1? that number is 8 bits, so the answer is 0! that’s what you wanted right?”
This can cause VERY tricky bugs
some languages where integer overflow happens
Java/Kotlin
C/C++
Rust
Swift
C#
SQL
R
Go
Dart
Python (only in numpy)
Some throw errors on overflow, some don’t, for some it depends on various factors. Look up how it works in your language!